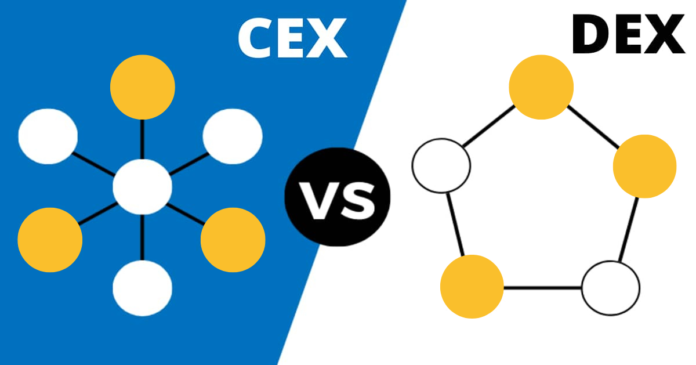
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges, By definition, any transaction that happens in a peer-to-peer fashion can be thought of as being a decentralized trade.
We’ll find out what decentralized exchanges are and why they have become a popular alternative to regular cryptocurrency exchanges.
For as long as we know investors have bought and sold cryptocurrencies using centralized exchanges. You find a good platform register an account complete the standard KYC process and start investing in digital assets that’s all there is to it.
Now a new kind of exchange is in town as of 2022. With the rising adoption of Defi, more and more users are migrating to decentralized exchanges that provide the complete opposite experience. These exchanges enforce neither verifications nor signups and at any given moment the crypto you trade is entirely under your control.
How decentralized exchanges work?
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges: How are decentralized exchanges decentralized and in what kind of way does their method of operation differ from centralized trading platforms?
By definition, any transaction that happens in a peer-to-peer fashion can be thought of as being a decentralized trade. If two crypto fans called bob and Alice trade Ethereum for let’s say tether with each other and the entire transaction takes place on a blockchain the trade is decentralized. If that were to happen through a third-party system like an exchange or a custodian the trade would be centralized.
So as long as we have peer-to-peer trading that stays at all times on the blockchain and interacts in no way with a centralized platform the swap in question is decentralized. Decentralized exchanges practice the same process with the core difference being that they mimic centralized trading platforms. Their goal is to provide a blockchain-powered platform that offers trading services and liquidity to crypto investors just like Binance or Coinbase do.
The way that they achieve that is by relying on the use of smart contracts. A group of instructions that, when certain conditions are met, are carried out automatically and independently. This means that dex operators can automate withdrawal deposits and trades without having to personally authorize them or initiate any actions on their part. Three key decentralized exchange formats have been made possible by smart contracts.
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges: Dexs with an on-chain order book, decks with an off-chain order book, and decks with an automated market maker. On-chain order books enable completely decentralized exchanges. Considering that all events and actions are recorded on the blockchain which ensures a completely transparent trading experience. However such exchanges are impractical since users have to pay even more fees and can be front run by other users who can view pending transactions on blockchain explorers.
By hosting their order books on a centralized system, exchanges with off-chain order books dial back decentralization. Orders on this type of exchange are processed by a non-decentralized offline entity rather than being stored on blockchain networks. The trades themselves are still carried out on a chain, though.
Related: Do Decentralized Oracles Matter? Why
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges: An exchange with an automated market maker is currently the newest and most well-liked choice. By utilizing game theory, and mathematical formulas, and wrapping them in smart contracts, AMMs outright reject order books and implement a fundamentally different method of processing and distributing liquidity.
Nearly every decentralized exchange nowadays uses automated market makers. The most famous implementation of uni swap is a trading platform that utilizes the constant product formula of x times y equals k, while x and y represent a trading pair of two different tokens k is an unchangeable constant that must be preserved at all times. Simply put the formula dictates that all changes in the trading pairs reserved balances should not change the constant product of k. This is made possible by charging fees for every trade and transferring it back to liquidity reserves. Which creates a counterbalance by adding a positive pressure to the k constant.
How do they acquire liquidity?
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges: Liquidity is the blood of every exchange it’s what keeps trading platforms alive and attracts new users. So dexes are decentralized how do they acquire liquidity in the first place? Decentralized exchanges mainly rely on liquidity suppliers who practice yield farming and liquidity mining. By offering them financial incentives, these users are encouraged to lend their crypto assets to a dex. The liquidity given to exchange is then used to fuel a trader’s token swap who has to pay a fee for the transaction. In appreciation for supplying the initial liquidity in the first place, a portion of this fee is returned to the liquidity providers.
This symbiotic relationship is what makes decentralized exchanges thrive in an ecosystem such as the crypto markets. Each of the three parties exchange operators, liquidity providers, and traders provides something and takes another thing in return. With all this talk we may have given you the impression that decentralized exchanges are perfect and that there’s nothing wrong with them but that couldn’t be farther from the truth.
Disadvantages of decentralized exchanges
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges: There are three notable disadvantages that affect users of nearly all skill levels and they include user experience, fees, and trading volume. Decentralized exchanges aren’t known for offering a great user experience. They’re clunky, difficult to use, and buggy. A crypto veteran might have an easier time trading on uni swap or sushi swap or pancake swap but a beginner will most likely fall at the very first step.
Newcomers tend to not understand how to perform a transaction. They can forget password seed phrases and lose access to their funds. Fees are another predominant issue that rarely goes away. Since trades are executed by smart contracts rather than the centralized systems employed by traditional exchanges traders pay higher fees on average. Fees on decentralized exchanges are not that bad but whenever a network is congested users can pay up to hundreds of dollars for a single trade.
Although decentralized exchanges have caught up with centralized ones in terms of liquidity they’re still dwarfed by industry giants like Coinbase and Binance. Liquidity is truly everything and when a dex does not have enough of it it’s better to stick with centralized trading platforms. Because of their high rates of slippage and empty order books in between significant price levels, illiquid markets are chaotic to trade.
Related: Why Decentralized Exchanges are the future of crypto trading?
Centralized vs Decentralized Exchanges: All in all decentralized exchanges are revolutionary platforms that have changed the crypto market forever. Some believe that DEXAs can turn crypto platforms totally independent from the real world by giving users a way to interact with each other solely through a blockchain. We have yet to see whether the new wave of exchanges will achieve that goal as there are still many obstacles. Fees are unbelievably high trading interfaces are still primitive and decentralized exchanges are nowhere near reaching the level of liquidity that centralized platforms offer. Once the Defi sector matures and developers focus more on building rather than marketing products during a euphoric market we will surely see a positive shift in tone. Until then only trading experts and crypto whales will have fun using decentralized exchanges. What do you think are decentralized exchanges going to take over centralized exchanges or not? Let us know in the comments below.